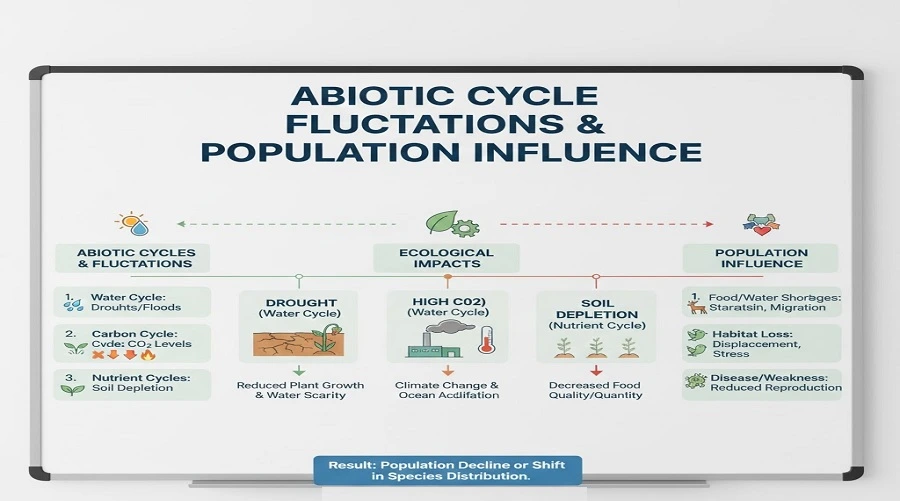
Understanding ecology calls for us to explain how fluctuations in abiotic cycles can influence populations.. Abiotic cycles along with the water cycle, carbon cycle, nitrogen cycle, phosphorus cycle, and oxygen cycle adjust the provision of crucial non-dwelling sources. When these cycles range because of natural version or human pastime, populace length, distribution, survival, and replica can change dramatically.
Table of Contents
What Are Abiotic Cycles?
Abiotic cycles (also known as biogeochemical cycles) describe the motion of chemical elements and compounds between living organisms and the non-residing surroundings (air, water, soil, rocks).
Major Abiotic Cycles
- Water (Hydrologic) Cycle
- Carbon Cycle
- Nitrogen Cycle
- Phosphorus Cycle
- Oxygen Cycle
To explain how fluctuations in abiotic cycles can influence populations, we have to observe how changes in resource availability affect survival and duplication.
Why Fluctuations Occur in Abiotic Cycles
Fluctuations occur due to:
- Seasonal modifications (rainfall, temperature)
- Natural events (droughts, floods, volcanic eruptions)
- Climate exchange
- Human sports (deforestation, industrial emissions, fertilizer use)
👉 These adjustments regulate aid availability, which without delay affects populations.
Key Abiotic Cycles and Their Influence on Populations
1. Water Cycle and Population Dynamics
The water cycle controls precipitation, evaporation, runoff, and groundwater availability.
How Water Cycle Fluctuations Affect Populations
- Droughts lessen plant increase → herbivore decline → predator decline
- Floods ruin habitats however may additionally growth vitamins
- Altered rainfall patterns affect breeding cycles
| Water Cycle Change | Population Effect |
|---|---|
| Drought | Reduced plant biomass, animal starvation |
| Excess rainfall | Habitat loss, disease spread |
| Seasonal rainfall | Migration and breeding timing |
Example:
Extended droughts lessen grass increase, inflicting herbivore populations to crash, accompanied by means of predator decline.
2. Carbon Cycle Fluctuations and Population Impact
The carbon cycle regulates carbon dioxide (CO₂) ranges, influencing photosynthesis and weather.
Key Effects on Populations
- Increased CO₂ → better plant growth (short term)
- Climate warming → habitat shifts
- Ocean acidification → marine population decline
| Carbon Cycle Change | Population Impact |
|---|---|
| High CO₂ levels | Climate stress on species |
| Reduced photosynthesis | Lower food availability |
| Ocean acidification | Coral and shellfish decline |
Important Point:
To explain how fluctuations in abiotic cycles can have an effect on populations, carbon imbalance is one of the most powerful drivers of worldwide population change.
3. Nitrogen Cycle and Ecosystem Populations
The nitrogen cycle resources plant life with usable nitrogen (nitrates, ammonium).
Population Effects
- Nitrogen deficiency → terrible plant increase
- Excess nitrogen → eutrophication
- Algal blooms → oxygen depletion → fish dying
| Nitrogen Level | Effect on Populations |
|---|---|
| Low nitrogen | Reduced plant & herbivore populations |
| Excess nitrogen | Algal blooms, aquatic death |
| Balanced nitrogen | Healthy ecosystems |
Example:
Fertilizer runoff increases nitrogen in lakes, causing algal blooms that kill fish populations.
4. Phosphorus Cycle and Population Stability
The phosphorus cycle impacts DNA, ATP, and cell membranes.
How Fluctuations Influence Populations
- Limited phosphorus → sluggish increase
- Excess phosphorus → eutrophication
- Soil depletion → agricultural decline
| Phosphorus Change | Population Effect |
|---|---|
| Low availability | Reduced growth & reproduction |
| High availability | Water pollution & species loss |
5. Oxygen Cycle and Population Survival
The oxygen cycle keeps tiers of oxygen for respiration.
Population Impacts
- Low oxygen → hypoxia → mass die-offs
- Aquatic oxygen loss → fish mortality
- Forest loss → decreased oxygen manufacturing
| Oxygen Level Change | Population Impact |
|---|---|
| Reduced oxygen | Reduced survival rates |
| Aquatic hypoxia | Fish population collapse |
How Abiotic Cycle Fluctuations Affect Population Size
To give an explanation for how fluctuations in abiotic cycles can have an impact on populations, consider those mechanisms:
1. Carrying Capacity Changes
- Resource discount lowers wearing potential
- Populations decline when limits are passed
2. Reproductive Rate Alteration
- Stress reduces fertility
- Abundant resources boom duplicate
3. Migration and Distribution Shifts
- Species pass to favorable environments
- Leads to range expansion or contraction
Human Impact on Abiotic Cycles and Populations
| Human Activity | Abiotic Cycle Affected | Population Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Deforestation | Carbon & oxygen | Habitat loss |
| Fossil fuels | Carbon | Climate-driven extinctions |
| Agriculture runoff | Nitrogen & phosphorus | Aquatic population collapse |
| Water extraction | Water cycle | Species displacement |
Human movements accelerate abiotic fluctuations, making populace responses extra severe and much less predictable.
Case Studies: Abiotic Cycles Influencing Populations
Case 1: Drought and African Herbivores
- Reduced rainfall → grass shortage
- Herbivore decline → predator decline
Case 2: Coral Reefs and Carbon Cycle
- Increased CO₂ → ocean acidification
- Coral bleaching → fish populace loss
Case 3: Lake Eutrophication
- Nitrogen & phosphorus growth
- Oxygen depletion → fish die-offs
Why This Topic Is Important in Ecology Exams
Students are regularly requested to explain how fluctuations in abiotic cycles can impact populations because it links:
- Ecosystem balance
- Population ecology
- Climate technology
- Human environmental effect
This topic appears frequently in biology, environmental technological know-how, and ecology tests.
Summary Table: Abiotic Cycles and Population Effects
| Abiotic Cycle | Main Resource | Population Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Water cycle | Freshwater | Survival & reproduction |
| Carbon cycle | CO₂ | Climate & food webs |
| Nitrogen cycle | Soil nutrients | Plant productivity |
| Phosphorus cycle | Minerals | Growth & energy |
| Oxygen cycle | Oxygen | Respiration & survival |
Summary
To provide an explain how fluctuations in abiotic cycles can influence populations., remember how changes in water, carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, and oxygen affect aid availability. These fluctuations adjust survival, reproduction, migration, and carrying ability, shaping population length, distribution, and long-term ecosystem balance.
Main questions to ask on this – explain how fluctuations in abiotic cycles can influence populations.
1. What are abiotic cycles?
Ans. Abiotic cycles are natural approaches that recycle non-dwelling elements like water, carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus through ecosystems.
2. Why do abiotic cycle fluctuations affect populations?
Ans. Because populations depend on solidity to get right of entry to crucial assets for survival and reproduction.
3. Which abiotic cycle maximum strongly affects populations?
Ans. The water and carbon cycles have the biggest worldwide impact because of weather.
4. How do humans affect abiotic cycles?
Ans. Through deforestation, pollutants, fossil gasoline use, and agriculture, causing speedy fluctuations.
5. Why is this subject matter critical in ecology?
Ans. It explains population modifications, species decline, and ecosystem imbalance, essential for conservation planning.