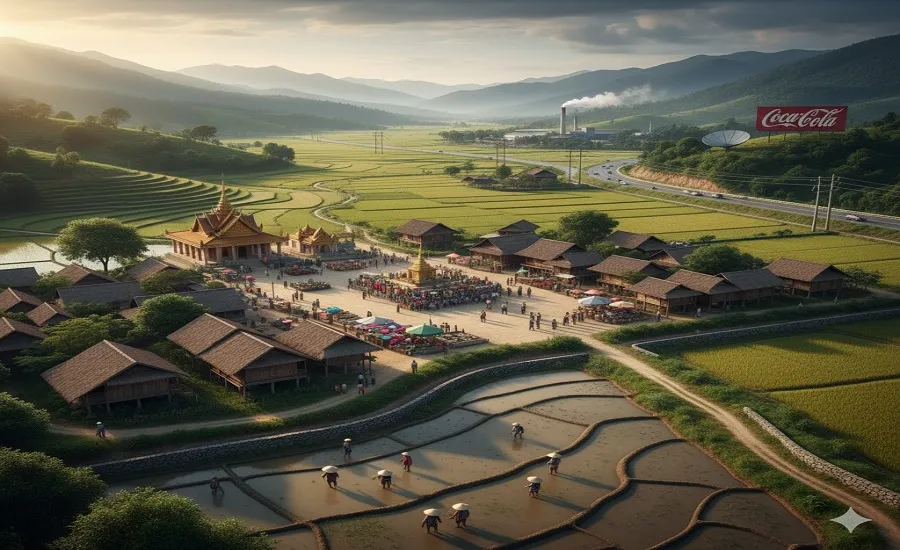
The concept of Cultural Landscape AP Human Geography is one of the most vital and often examined topics within the AP Human Geography curriculum. It explains how human subculture interacts with the herbal environment and leaves seen, lasting marks at the Earth’s floor. From structure and agriculture to language, faith, and concrete making plans, cultural landscapes reveal who we’re, where we got here from, and the way societies shape locations.
Table of Contents
What Is Cultural Landscape in AP Human Geography?
In cultural landscape AP Human Geography, a cultural panorama refers to the visible imprint of human activity at the natural landscape.
Definition
A cultural panorama is a geographic location that has been changed via human beliefs, values, and practices.
This includes:
- Buildings
- Farms
- Cities
- Roads
- Religious systems
- Patterns of land use
The idea emphasizes that humans are active dealers shaping the Earth, no longer simply a passive population.
Origin of the Cultural Landscape Concept
The concept of cultural panorama AP Human Geography came through Carl Sauer, a famous cultural geographer.
Carl Sauer’s Theory
- Natural panorama + human subculture = Cultural landscape
- Culture acts because the agent
- The land is the medium
- The cultural landscape is the end result
This theory is a center basis of AP Human Geography.
Key Characteristics of Cultural Landscapes

The cultural landscape AP Human Geography concept has numerous defining traits:
1. Human Modification
Humans modify landscapes thru:
- Agriculture
- Urbanization
- Transportation
- Industry
2. Cultural Values
Landscapes reflect:
- Religion
- Language
- Traditions
- Economic systems
3. Visible Evidence
Cultural landscapes can be:
- Seen
- Mapped
- Studied geographically
4. Change Over Time
Cultural landscapes evolve as:
- Technology advances
- Cultures migrate
- Societies modernize
Types of Cultural Landscapes
Understanding different sorts is vital for cultural landscape AP Human Geography exam questions.
1. Rural Cultural Landscapes
- Farms
- Villages
- Agricultural fields
- Irrigation structures
Example: Rice terraces in Asia
2. Urban Cultural Landscapes
- Skyscrapers
- Street layouts
- Business districts
- Housing patterns
Example: New York City skyline
3. Religious Cultural Landscapes
- Temples
- Churches
- Mosques
- Pilgrimage routes
Example: Vatican City
4. Political Cultural Landscapes
- Borders
- Capital cities
- Monuments
- Government buildings
Example: Washington, D.C.
Examples of Cultural Landscapes (AP Exam Friendly)
Here are some excessive-scoring examples often utilized in cultural landscape AP Human Geography answers:
| Example | Type | Cultural Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Rice terraces (Asia) | Agricultural | Adaptation to environment |
| European cathedrals | Religious | Christian cultural dominance |
| American suburbs | Urban | Automobile culture |
| Arabic calligraphy architecture | Religious | Islamic traditions |
| Latin American plazas | Political | Spanish colonial influence |
Cultural Landscape vs Natural Landscape
This comparison is regularly tested in cultural landscape AP Human Geography questions.
| Aspect | Cultural Landscape | Natural Landscape |
|---|---|---|
| Created by | Humans | Nature |
| Examples | Cities, farms, roads | Mountains, rivers |
| Change speed | Fast | Slow |
| Reflects culture | Yes | No |
Role of Culture in Shaping Landscapes
Culture affects landscapes in more than one approaches:
Religion
- Churches dominate European cities
- Mosques form Middle Eastern skylines
Language
- Road signs
- Place names
- Store names
Economics
- Industrial zones
- Commercial centers
- Agricultural regions
Politics
- Capital towns
- National monuments
- Borders and walls
All of these make the cultural panorama AP Human Geography framework stronger.
Cultural Landscape and Diffusion
Cultural diffusion performs a main role in shaping landscapes.
Types of Diffusion
- Relocation diffusion: Migrants convey cultural styles
- Expansion diffusion: Cultural trends unfold outward
Example
Spanish colonization unfold:
- Catholic church buildings
- Plaza-targeted cities
- European architecture
Globalization and Cultural Landscapes

Globalization has transformed cultural panorama AP Human Geography styles international.
Positive Effects
- Improved infrastructure
- Cultural alternate
Negative Effects
- Loss of local identity
- Cultural homogenization
Example: Fast-meals chains performing globally
Cultural Landscape in AP Exam Questions
The cultural panorama AP Human Geography topic seems in:
- Multiple-choice questions
- FRQs (Free Response Questions)
How to Score High
- Use precise examples
- Link culture to panorama
- Mention Carl Sauer
- Compare regions
Important Vocabulary (Must Remember)
- Cultural landscape
- Built surroundings
- Sense of location
- Placelessness
- Cultural diffusion
- Sequent occupance
Knowing those phrases boosts AP exam rankings.
Why Cultural Landscape Is Important
The cultural panorama AP Human Geography concept allows students:
- Understand human-environment interplay
- Analyze spatial styles
- Recognize cultural variety
- Interpret worldwide development
It explains why places appear the manner they do.
Modern Examples of Cultural Landscape Changes
- Smart cities
- Renewable electricity farms
- Urban sprawl
- Gentrification
These show that cultural landscapes are dynamic, not static.
Summary
The cultural landscape AP Human Geography concept explains how human subculture shapes the Earth’s floor. Introduced through Carl Sauer, it highlights visible human changes like cities, farms, and spiritual web sites. Understanding cultural landscapes is vital for AP exam achievement.
Main questions to ask on this “Cultural Landscape AP Human Geography“
1. What is a cultural panorama in AP Human Geography?
Ans. A cultural landscape is the visible imprint of human interest and culture in the herbal environment.
2. Who added the cultural panorama concept?
Ans. The concept was introduced by using Carl Sauer, a cultural geographer.
3. Why is cultural landscape important for the AP examination?
Ans. It frequently appears in FRQs and MCQs and explains human-surroundings interplay.
4. What is an instance of a cultural panorama?
Ans. Examples consist of rice terraces, urban skylines, and non secular monuments.
5. How does globalization have an effect on cultural landscapes?
Ans. Globalization can cause cultural homogenization and loss of neighborhood identity.